Hellopeter
For many South African businesses, online reputation is still treated as a brand or marketing concern, something handled by communications teams, monitored through sentiment dashboards, and addressed when crises emerge.
This categorization is fundamentally incorrect and increasingly dangerous.
In today's digital-first environment, online reputation represents a material business risk that affects revenue generation, customer acquisition costs, regulatory exposure, investor confidence, and long-term market positioning. Public complaints, unresolved reviews, and visible patterns of customer dissatisfaction now influence how customers, partners, regulators, investors, and prospective employees assess your business.
Reputation risk is no longer hypothetical or abstract. It is visible, searchable, cumulative, and measurable. It sits on the first page of Google when prospects research your company. It appears in due diligence reports when investors evaluate your business. It influences enterprise procurement decisions when your sales team reaches the final stages of competitive evaluations.
This article examines why online reputation has evolved into a core business risk in the South African context, how it manifests across different business functions, and what executive leadership should understand about managing this exposure systematically. Understanding what negative reviews really cost businesses is the first step toward treating reputation as the strategic risk it has become.
Why Reputation Has Become a Business Risk
Understanding the shift from "reputation management" to "reputation risk" requires recognizing fundamental changes in how business credibility is established and evaluated.
The Shift from Controlled Messaging to Public Accountability
Twenty years ago, companies controlled their reputation narrative through advertising, PR, and controlled communications. Customer experiences were largely private, complaints happened through call centers, in-person interactions, or written letters that remained invisible to the broader market.
Today, every customer interaction has the potential to become public knowledge. A single unresolved complaint can reach thousands of prospective customers. Patterns of poor service become visible trends that influence market perception. Company responses (or silence) signal organizational culture and governance quality to observers.
This shift means reputation is no longer what you say about yourself, it's what your customers say about you, publicly and permanently. As we explore in why silence on public complaints damages brand credibility, the absence of response often communicates more than the complaints themselves.
Unlike Traditional Reputational Threats, Online Reputation Doesn't Require a Crisis
Traditional reputation damage typically resulted from acute events: product recalls, safety incidents, regulatory violations, executive scandals, or PR crises. These were dramatic, visible, and required crisis management protocols.
Online reputation risk builds differently. It accumulates quietly through patterns of unresolved complaints, unanswered feedback, inconsistent service quality, and visible disengagement from customer concerns. There's no single catastrophic event, just steady erosion of trust that compounds over time.
This gradual accumulation is precisely what makes it dangerous. By the time leadership recognizes the impact on conversion rates, enterprise deal progression, or market position, the damage has already materialized across multiple business functions.
Reputational Signals Reveal Deeper Organizational Issues
What appears as "negative reviews" or "customer complaints" often signals more fundamental problems:
Weak Customer Accountability Systems: When complaints go unanswered or unresolved, it indicates missing feedback loops, unclear ownership of customer issues, inadequate escalation processes, or disconnection between customer-facing teams and decision-making authority.
Poor Operational Visibility: Persistent complaints about the same issues suggest that leadership lacks real-time visibility into operational failures, customer-facing teams cannot influence product or service improvement, or quality control mechanisms are insufficient or ignored.
Governance Gaps: Public patterns of unresolved complaints raise questions about whether customer commitments are tracked and honored, whether accountability exists for customer outcomes, and whether leadership monitors and acts on customer feedback systematically.
These are not marketing problems, they are operational, governance, and strategic execution problems that manifest as reputational damage.
The South African Context: Regulatory and Cultural Factors
The South African business environment presents specific factors that elevate online reputation from perception management to business risk.
High Consumer Rights Awareness
South African consumers are increasingly sophisticated about their legal rights under the Consumer Protection Act (CPA). They understand concepts like fair dealing, reasonable conduct, disclosure obligations, and recourse options.
When businesses fail to meet these expectations, consumers don't just complain privately, they escalate publicly and often involve regulatory bodies. This means customer complaints frequently intersect with compliance obligations, creating regulatory exposure that extends beyond customer satisfaction.
Complaints as Regulatory Signals
For businesses in regulated industries, financial services, insurance, telecommunications, healthcare, property, public complaints are not just customer service issues. They can be:
- Early indicators of systematic compliance failures
- Evidence in regulatory investigations or enforcement actions
- Patterns that trigger ombudsman scrutiny
- Material that influences licensing or registration reviews
- Information that affects regulatory reporting requirements
When the Financial Sector Conduct Authority (FSCA), National Consumer Commission (NCC), or industry ombudsman reviews your business, they increasingly consider public complaint patterns as risk indicators.
Trust as Currency in Emerging Markets
South Africa's economic environment, characterized by economic uncertainty, fraud concerns, and variable service quality across industries makes trust a critical competitive differentiator. In markets where many consumers have experienced poor service or dishonest business practices, demonstrated trustworthiness becomes valuable.
Public handling of complaints signals whether your business can be trusted when things go wrong which is often more important than whether problems occur in the first place. This is why understanding whether negative reviews are actually hurting your business requires looking beyond surface metrics to trust indicators.
Digital Transparency Expectations
South African consumers, particularly in urban and middle-class markets, increasingly expect businesses to engage transparently online. Silence or defensive responses to public complaints signal unwillingness to be held accountable, creating reputational damage that extends beyond the specific complaint.
How Reputation Risk Impacts Different Business Functions
Reputation risk doesn't remain contained in the marketing department, it creates friction across the entire organization.
Sales and Revenue Impact
Conversion Rate Erosion: Prospects research companies before engaging. Negative reviews without responses create doubt during the decision-making process. Even strong sales efforts can't overcome reputational concerns that prospects discover independently.
Increased Customer Acquisition Cost: When reputation issues exist, marketing must work harder to generate the same conversion outcomes. More touchpoints are required, more trust-building is necessary, and more objection handling extends sales cycles, all increasing cost per acquisition.
Deal Velocity Reduction: Enterprise sales cycles lengthen when procurement teams discover unresolved complaints during vendor evaluation. Questions about service quality, customer support capabilities, and organizational reliability must be addressed repeatedly.
Competitive Disadvantage in Final Evaluations: When multiple vendors reach the final stage of competitive evaluations, reputation becomes a decisive factor. The vendor with better demonstrated customer accountability wins, even with comparable products.
Enterprise and B2B Relationship Risk
Partner Hesitation: Business partners evaluating collaborations assess reputational risk as part of partnership due diligence. Patterns of unresolved complaints signal operational unreliability that creates risk for the partner's own reputation.
Procurement Red Flags: Large organizations increasingly include reputation assessment in vendor evaluation frameworks. Public complaint patterns can eliminate vendors from consideration or require additional compliance validation.
Contract Renewal Vulnerability: Existing enterprise customers monitoring public reputation may reconsider renewals if they see patterns suggesting service quality degradation or poor customer treatment.
Regulatory and Compliance Exposure
Ombudsman Scrutiny: Industry ombudsman services monitor public complaint patterns. High volumes of unresolved complaints about similar issues can trigger proactive investigations.
Regulatory Examination: Regulators increasingly use public information as risk indicators. Systematic complaint patterns may influence examination priorities or licensing reviews.
Consumer Protection Enforcement:The National Consumer Commission can investigate businesses showing patterns of CPA violations visible through public complaints.
Litigation Risk: Public complaints create discoverable evidence in consumer litigation. Patterns of similar complaints strengthen class action viability or regulatory enforcement cases.
Operational and Strategic Impact
Talent Acquisition and Retention: Prospective employees research company culture and values. Public patterns of customer mistreatment signal organizational culture issues that affect employer brand and talent quality.
Investor and Stakeholder Confidence: For businesses seeking investment or strategic partnerships, due diligence increasingly includes reputation assessment. Systematic complaint patterns raise questions about management quality and operational excellence.
Market Position Erosion: In competitive markets, reputation advantages compound. Businesses with better demonstrated customer accountability capture market share from competitors struggling with reputational drag.
Measuring Reputation as a Business Risk
Unlike traditional business risks that appear in financial statements or compliance reports, reputation risk requires different measurement approaches.
Leading Indicators of Reputation Risk:
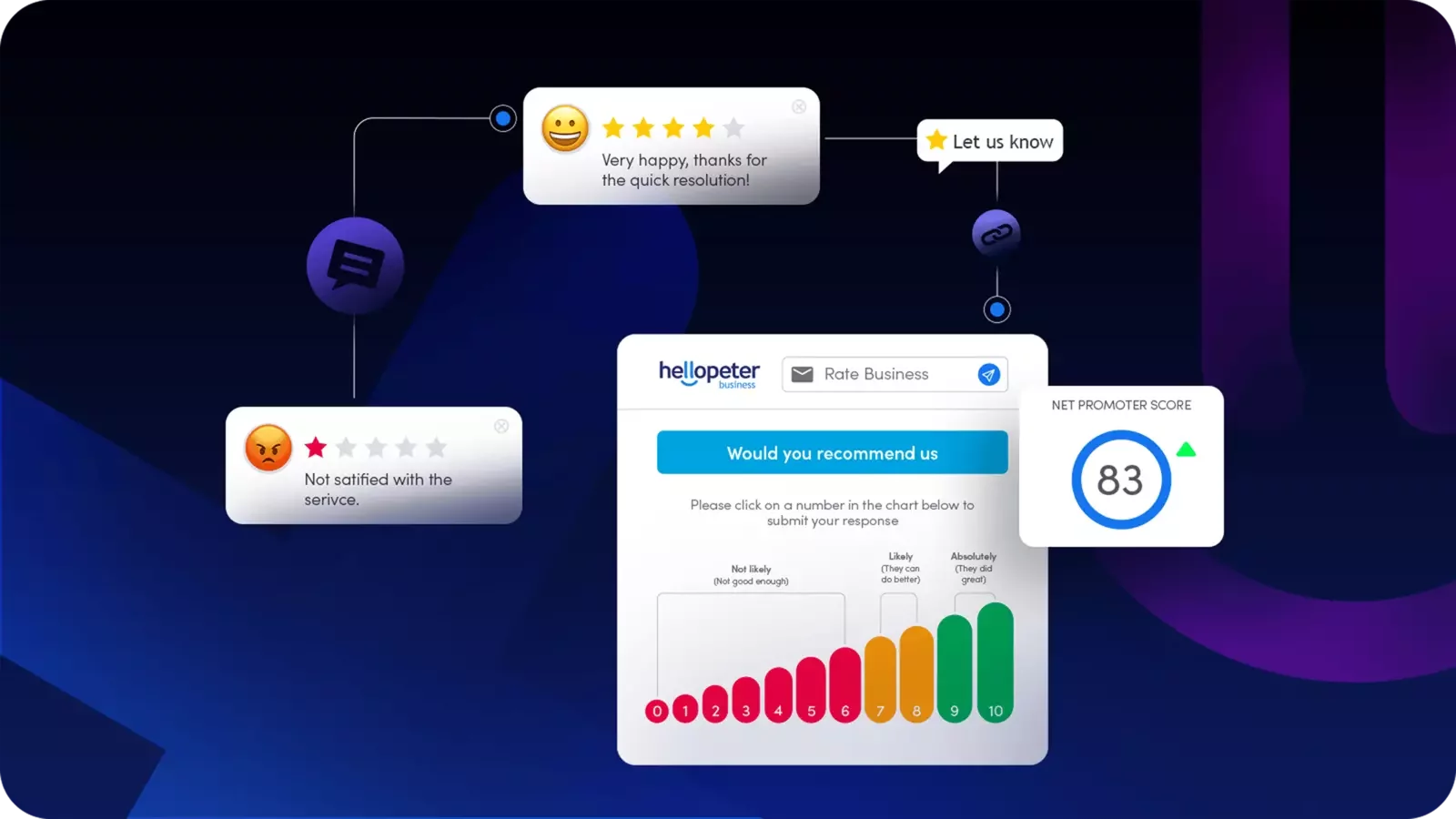
Response Rate to Public Complaints: Percentage of public complaints receiving company response. Industry benchmark: well-managed businesses respond to 80%+ of public complaints on platforms like Hellopeter.
Resolution Rate: Percentage of complaints marked as resolved by customers. Low resolution rates signal systematic service failures or inadequate complaint handling.
Response Time: Average time between complaint publication and company engagement. Delays signal poor monitoring or organizational inertia.
Complaint Topic Concentration: Multiple complaints about identical issues indicate systematic operational problems requiring executive attention.
Sentiment Trend: Directional movement in complaint tone and severity. Increasing frustration levels signal deteriorating customer relationships.
Public Engagement Quality: Whether responses demonstrate accountability versus defensiveness. Defensive responses often damage reputation more than silence.
Lagging Indicators Showing Materialized Risk:
Conversion Rate Decline: Decreasing conversion despite stable traffic suggests reputation-driven prospect hesitation.
Sales Cycle Extension: Lengthening time-to-close without other market changes indicates increased trust-building requirements.
Customer Acquisition Cost Increase: Rising CAC without corresponding market changes suggests reputational friction.
Lost Deal Analysis: Competitive losses citing "service concerns" or "reputation issues" in feedback.
Ombudsman Complaint Volume: Escalations to industry ombudsman services indicating failure to resolve issues internally.
Managing Reputation as a Risk Discipline
Treating online reputation as a business risk rather than a marketing concern requires systematic management approaches.
Establish Clear Ownership and Accountability
Reputation risk should have executive ownership, typically reporting to the COO, CFO, or Chief Risk Officer rather than the CMO. This signals that reputation is a business risk requiring operational accountability, not just brand management.
Create Visibility and Monitoring Systems
Risk cannot be managed without visibility. Businesses need systematic monitoring of public complaints and reviews, automated alerting for new complaints or escalating issues, regular executive reporting on reputation metrics, and integration of reputation data into business intelligence systems.
Platforms like Hellopeter for Business provide centralized visibility into public customer feedback, making patterns recognizable and response tracking measurable.
Define Response Protocols and SLAs
Managing reputation risk requires consistent, timely engagement. This means clear SLAs for acknowledging public complaints, escalation paths for complex or sensitive issues, approval workflows balancing speed with appropriate review, and quality standards ensuring responses demonstrate accountability rather than defensiveness.
Connect Reputation Data to Operational Improvement
Public complaints should feed directly into operational and product improvement processes. This requires regular review of complaint themes by relevant department leaders, systematic root cause analysis of recurring issues, accountability for addressing systematic problems generating complaints, and tracking whether operational improvements reduce specific complaint categories.
Integrate Reputation Assessment into Strategic Decisions
When evaluating market expansion, product launches, partnership opportunities, or operational changes, include reputation impact assessment: "How will this decision affect customer trust?" "What reputational risks does this create?" "How will we monitor and manage those risks?"
Train and Empower Customer-Facing Teams
Frontline teams need authority and tools to prevent issues from becoming public complaints. This requires clear escalation authority for resolving issues before they escalate, training on identifying patterns that signal systematic problems, and empowerment to address complaints publicly when appropriate.
Common Executive Misconceptions About Online Reputation Risk
Several persistent misconceptions prevent businesses from managing reputation risk effectively.
Misconception #1: "Negative Reviews Are Just Noise"
Reality: While individual complaints vary in validity, patterns of similar complaints are signal, not noise. They indicate systematic issues requiring operational attention.
Misconception #2: "Responding Publicly Amplifies Problems"
Reality: Public responses demonstrate accountability and control narrative risk. Silence allows complainants and observers to control the narrative instead.
Misconception #3: "We Handle Complaints Privately, So Public Reputation Doesn't Matter"
Reality: Private resolution is invisible to observers. Without public acknowledgment, markets perceive inaction regardless of private efforts.
Misconception #4: "Our Target Market Doesn't Look at Reviews"
Reality: B2B buyers, enterprise procurement, and high-value consumers actively research vendor reputation. The more valuable the relationship, the more due diligence occurs.
Misconception #5: "We Can't Control What Customers Say Online"
Reality: While you can't control complaints, you completely control your response. Engagement quality determines whether complaints damage or demonstrate credibility.
Misconception #6: "This Is a Marketing Problem"
Reality: Reputation risk stems from operational failures, service gaps, and governance issues. Marketing cannot solve problems it doesn't create.
The Strategic Opportunity in Reputation Risk Management
While this blog frames online reputation as a risk, properly managed it becomes a competitive advantage.
Demonstrated Accountability Builds Trust
Businesses that engage openly with complaints signal organizational maturity, customer-centricity, and governance quality. In markets where many competitors avoid accountability, this differentiation is valuable.
Public Problem-Solving Demonstrates Competence
When prospects see your business acknowledging and resolving issues publicly, they gain confidence in your ability to handle problems when they arise—which builds trust more effectively than claiming perfection.
Complaint Intelligence Drives Improvement
Public feedback provides unfiltered market intelligence about product gaps, service failures, and operational weaknesses. Companies that systematically act on this intelligence improve faster than competitors ignoring the signal.
Reputation Excellence Enables Premium Positioning
In mature markets, reputation for reliability and customer accountability supports premium pricing and reduces price-based competition. Customers pay for demonstrated trustworthiness.
Key Takeaways
Online reputation is a material business risk requiring executive oversight and systematic management. Reputation risk manifests across sales, regulatory exposure, enterprise relationships, and strategic positioning. South African regulatory and cultural context elevates reputation from perception to compliance concern.
Systematic complaint patterns signal operational and governance weaknesses requiring attention. Managing reputation risk requires visibility, accountability, response protocols, and operational integration. Public engagement with complaints demonstrates organizational maturity and controls narrative risk.
Reputation risk, properly managed, becomes competitive advantage through demonstrated accountability.
Conclusion
Online reputation is no longer a soft metric managed by marketing teams. It is a compounding business risk that requires the same systematic oversight, measurement, and management as financial risk, operational risk, or compliance risk.
For South African businesses operating in an environment of high consumer rights awareness, regulatory scrutiny, and digital transparency expectations, the cost of treating reputation as secondary concern continues to increase.
The businesses that recognize reputation as a core risk discipline, establishing visibility, accountability, and systematic response protocols will build sustainable competitive advantage through demonstrated trustworthiness.
The alternative is allowing reputation to deteriorate until it materially constrains growth, increases operational costs, and creates regulatory exposure that could have been prevented through systematic engagement.
The question for executive leadership is not whether to manage online reputation risk, but whether to manage it proactively before it constrains business outcomes, or reactively after it already has.
Ready to manage reputation as a business risk? Explore Hellopeter for Business to gain visibility into your public reputation and establish systematic response protocols.
Disclaimer:
This article is for informational purposes only and does not constitute legal, financial, or professional advice. HelloPeter makes no warranties regarding the accuracy or completeness of the information provided. Readers should conduct independent research and consult qualified professionals before making financial decisions. HelloPeter is not liable for any losses or damages arising from reliance on this information or interactions with third-party businesses. Consumer reviews on www.hellopeter.com represent individual opinions and should be considered alongside other sources when evaluating businesses.
RELATED ARTICLES
How to Request a Review Update: From Complaint to Resolved

Why Black Friday Customer Experience Beats The Discounts

How Super Communications Got to Rank #1 in 3 Industries on Hellopeter
UP NEXT
7 THINGS CUSTOMERS CHECK ONLINE BEFORE BUYING FROM YOU THIS BLACK FRIDAY